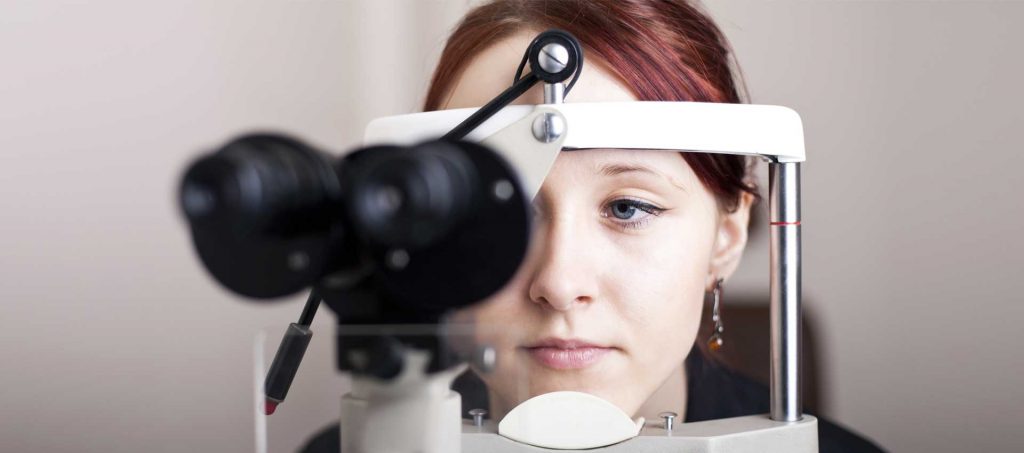
ITU, in collaboration with the Ministry of Health and Social Action of Senegal, is piloting an innovative solution to enhance the accessibility of timely diabetic retinopathy (DR) diagnosis for patients.
We are pleased to announce the launch of a pilot of our AI solution for early detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Senegal in partnership with ITU/WHO with support from the Ministry of Health, Senegal and Sanofi.
ITU in collaboration with WHO and Sanofi are supporting the government of Senegal to address Diabetic Retinopathy – a global healthcare challenge whose resolution is well in line with the UN’s Universal Health Coverage goals. The project aims to identify and implement an end-to-end innovative telemedicine system for detection of the diabetic retinopathy (DR) in Senegal in order to increase the number of the Senegal diabetic patients that have access to screening tools for preventing and reducing this diabetes complication that affects the eyes.
According to IDF there were 135.600 cases of diabetes in Senegal in 2017. Prevention of vision loss requires early detection via regular eye exams and screening for DR by a trained ophthalmologist or specialist. However, given the large numbers, there are not sufficient specialists globally to screen everyone at risk. This innovative solution will allow the ophthalmologists to remotely diagnose the DR using the digital images of the retina acquired through a conventional fundus camera. The technical solution will provide the component (Website) for the remote diagnosis of the DR by the ophthalmologists and also the Al component for the automatic diagnosis of the DR, the dashboard for the services monitoring and control and an interface for sending the eye images to the eye processing component.

The objective of this project is to do a pilot of the AI solution for DR developed by Xtend.AI and taking a systemic approach of the entire health ecosystem around this intervention. ITU/WHO would like to understand the issues around the possible uptake of this model, if the model can work for other clinics and countries and how it can be scaled up to entire Sub-Saharan region and beyond.
The solution model will include:
- the entire process from initial DR diagnosis to recommendation for subsequent follow up and communication of the results to patient and doctors
- the technical solution for the detection of DR including the technology and the deployment model
- the human capacity resources with required level of technical and medical expertise
The solution model will be deployed in few clinics selected by the Ministry of Health as “diabetes and hypertension clinics using IT (MCDH)”. The clinics are located outside Dakar in different parts of the country, both urban and rural areas. The objective is to do screening and to ensure follow up for all diabetic patients in the clinics with the ultimate goal of helping the diabetic people in detecting early signs of DR.
In parallel we will engage with telemedicine working groups in Senegal to identify the regulatory and ethical issues to be considered especially related to data protocols and data privacy and safety. We will introduce in this process a group of ophthalmologists that will compare the results of the automatic detection component of the tool with their own diagnosis.
The Ministry of Health and Social Action from Senegal through its eHealth department will manage the project internally.
The initial launch and deployment of the project was delayed due to the COVID pandemic to the first quarter. The solution has been successfully deployed and is in use in several clinics. The solution is actively being tested currently with results of the field trial expected by second quarter of 2023.